
With the help of nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, a research group led by Prof. WANG Hui from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has prepared a carbon-covered hollow cuprous oxide high-efficiency catalyst by using the solvent autocarbonylation reduction strategy, which provided a new solution for the electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction reaction (CO2RR) in the preparation of multicarbon (C2+) products.
The results were published in Advanced Functional Materials.
Excessive carbon dioxide emissions are a global problem. Converting CO2 into chemicals and fuels through CO2RR not only helps the environment but also supports China's "dual-carbon" target. Progress has been made in producing single carbon (C1) products such as carbon monoxide and formic acid from CO2RR. However, current CO2RR efficiency in producing C2+ products is low, creating a need for catalysts that can improve efficiency and selectivity.
In this study, the researchers developed a specialized nanoreactor called nitrogen-doped carbon shell-protected hollow cuprous oxide (H-Cu2O@C/N) using a solvent autocarbonation reduction strategy.
This nanoreactor enhancement helps increase the amount of key intermediates (*CO) on the catalyst surface, which accelerates the production of C2+ products through a chemical reaction.
When tested in a membrane electrode assembly (MEA) electrolyzer, the H-Cu2O@C/N nanoreactor achieved impressive results, with a 75.9% efficiency in producing C2+ products and a high current density of 248.8 mA·cm-2. This demonstrates the effectiveness of the catalysts in CO2RR conversion.
To further understand this process, the research team conducted detailed studies. These results confirmed that the C/N inclusions prepared by solvent autocarbon reduction strategy can effectively protect the Cu+ active species and ensure their catalytic stability.
This work provides an efficient and feasible way to optimize the catalyst structure for highly selective CO2RR preparation of C2+ products.
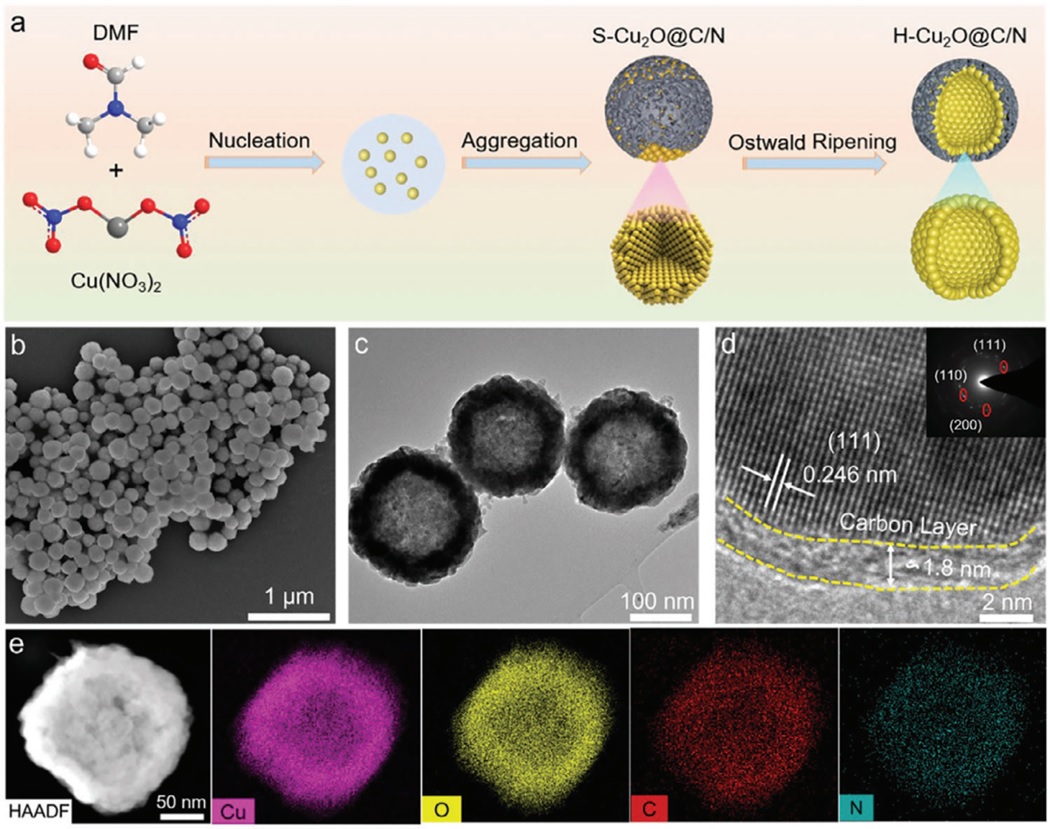
Synthesis schematic and characterization of H–Cu2O@C/N. a. Schematic of the synthetic process for H–Cu2O@C/N; b. SEM image; c. TEM image; d. HRTEM image, and the corresponding selective area electron diffraction pattern (inset) of H–Cu2O@C/N. (Image by WANG Hui)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

